A Single Dose of Creatine Increases Cognitive Processing Speed by 24.5% Within 3.5 Hours
The brain boost nobody talks about.

This article originally appeared on Focal Points and was republished with permission.
Guest post by Nicolas Hulscher, MPH
A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial found that creatine rapidly enhanced brain bioenergetics and improved cognitive performance during sleep deprivation, with effects lasting up to nine hours.
Creatine has long been regarded as just a muscle supplement — something for the gym that requires weeks of “loading” to saturate muscle stores. A recent randomized trial overturns that assumption.
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial published in Scientific Reports, researchers gave healthy young adults a single high oral dose of creatine monohydrate (0.35 g/kg — roughly 20 grams for most adults) during 21 hours of sleep deprivation. They then tracked both cognitive performance and real-time brain energy metabolism using advanced MR spectroscopy.
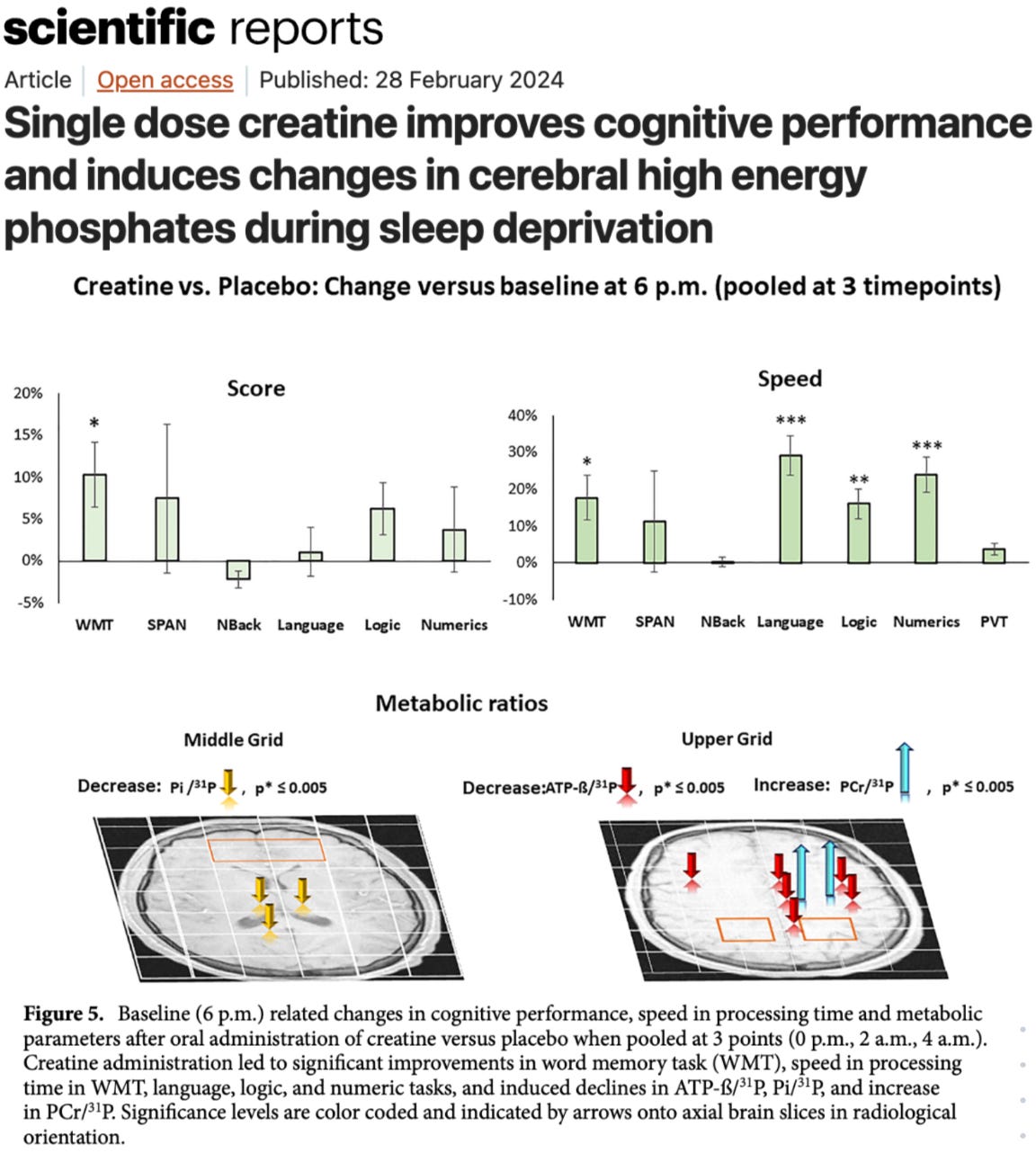
The results were not subtle. At the first post-dose assessment — approximately 3.5 hours after ingestion — participants demonstrated a 24.5% improvement in numeric processing speed (p = 0.0003). When data were pooled across all three overnight assessments (0 a.m., 2 a.m., 4 a.m.), language processing speed improved by 29.1% — the largest cognitive gain observed in the trial. And the effect didn’t fade quickly. Improvements in processing speed and task performance persisted across the next two measurement points — extending roughly nine hours after ingestion.
Just as important, the cognitive findings were mirrored by measurable metabolic shifts inside the brain. Creatine increased cerebral total creatine levels, prevented the typical sleep deprivation–induced drop in the PCr/Pi ratio (a marker of cellular energy stress), stabilized brain pH, and reduced subjective fatigue compared to placebo. In other words, this wasn’t just a behavioral effect — spectroscopy confirmed that high-energy phosphate metabolism itself was altered. The brain’s ATP buffering system appeared more resilient under stress.
In conclusion, a single ~20g dose of creatine rapidly enhanced brain bioenergetics and significantly improved cognitive performance during sleep deprivation, with effects sustained for up to nine hours.
Epidemiologist and Foundation Administrator, McCullough Foundation
Support our mission: mcculloughfnd.org
Please consider following both the McCullough Foundation and my personal account on X (formerly Twitter) for further content.
Copyright 2026 Focal Points